A study published last month confirmed what we already know: Americans across all demographics are increasingly getting their news from Facebook and Twitter. Nearly two-thirds of Facebook and Twitter users saying they use those social platforms to get news, with Twitter users particularly using it for breaking news.
But how are these users actually using the platform? How do they share news and what accounts do they follow? A new Pew snapshot susses out a few different behaviors. Not all Twitter users tweet about the news, for instance, but for those who do, nearly half their tweets on average were news-related.
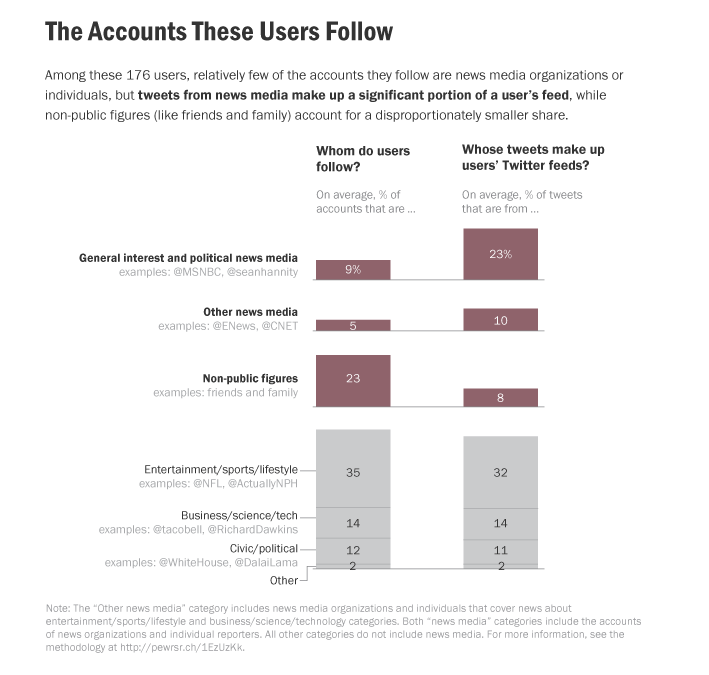
When posting about news, users were more likely to retweet than write an original post. On average, news media accounts made up about 9 percent of the accounts these users followed — but tweets from these accounts constituted 23 percent of these users’ feeds.
Of these news-tweeters sampled, the most popular topics were entertainment, sports, and then government and politics:
These findings come from a small but “representative” sample: for this study, Pew followed the Twitter activity of 176 U.S. adults with publicly accessible handles during a random four-week period between August 2014 and February 2015. Its survey suggests that many Twitter users are still just sporadic posters, with most in the 176-person sample tweeting just a few times a week or less.

The full post is available here with an explanation of the methodology and the study’s limitations.
Leave a comment